
When this equation is satisfied, X-rays scattered by the atoms in the plane of a periodic structure are in phase and diffraction occurs in the direction defined by the angle θ.In the simplest instance, an X-ray diffraction experiment consists of a set of diffracted intensities and the angles at which they are observed. In this equation, n is an integer, λ is the characteristic wavelength of the X-rays impinging on the crystallize sample, d is the interplanar spacing between rows of atoms, and θ is the angle of the X-ray beam with respect to these planes. The Bragg equation, nλ = 2dsinθ is one of the keystones in understanding X-ray diffraction. X-ray diffraction techniques have, therefore, been widely used as an indispensable means in materials research, development and production. NTP Technical Report on the Toxicology Studies of Cobalt Metal (CASRN ) in F344/N Rats and B6C3F1/N.
COBALT X RAY DIFFRACTION PATTERN SERIES
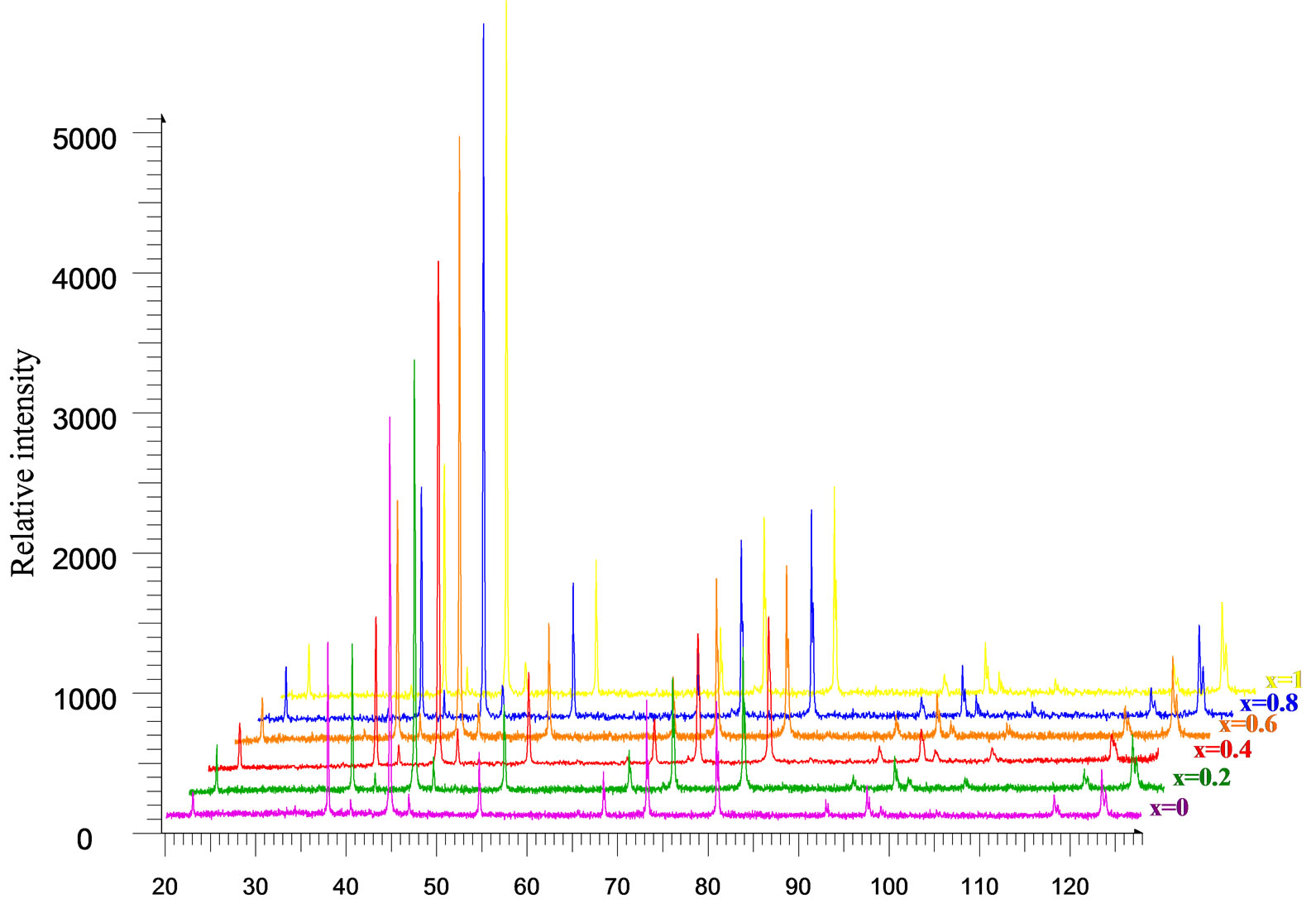
The properties and functions of materials largely depend on the crystal structures. X-ray Diffraction Pattern of Cobalt Metal. X-ray reference powder patterns and structures have been determined for a series of cobalt- and tungsten-containing cubic alkaline-earth perovskites, (BaxSr1-x) Crystal Chemistry, X-ray Diffraction Reference Patterns, and Band Gap Studies for (BaxSr1-x)2CoWO6 (x0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.5, 0.7, 0. X-ray diffraction techniques are superior in elucidating the three-dimensional atomic structure of crystalline solids. X-ray diffraction techniques are used for the identification of crystalline phases of various materials and the quantitative phase analysis subsequent to the identification. Rigaku has developed a range of X-ray diffractometers, in co-operation with academic and industrial users, which provide the most technically advanced, versatile and cost-effective diffraction solutions available today. From research to production and engineering, XRD is an indispensable method for materials characterization and quality control. X-ray diffraction (XRD) is one of the most important non-destructive tools to analyze all kinds of matter-ranging from fluids, to powders and crystals. The intensity in vertical axis is measured counts per. As shown, the X-ray diffraction pattern is distinct for each different phase. Quartz, cristobalite, and glass are all different phases of SiO 2 They are chemically identical, but the atoms are arranged differently. The analyzed material is finely ground, homogenized, and average bulk composition is determined. Each phase produces a unique diffraction pattern A phase is a specific chemistry and atomic arrangement. to the X-ray absorption spectrum of the tetrahedral and octahedral cobalt sites. X-ray diffraction (XRD) pattern of cobalt powder sample, revealing the simple cubic crystalline metallic cobalt oxide nanoparticles. Empyrean 2 (PANalytical) X-ray Diffraction System (Cobalt) Cobalt anode X-ray tube to minimise fluorescence from iron-containing samples that occurs when using. X-ray powder diffraction (XRD) is a rapid analytical technique primarily used for phase identification of a crystalline material and can provide information on unit cell dimensions. Determine the three dimensional structure of matter sity of an X-ray diffraction peak in the vicinity of an absorption edge.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
